Aptima® HPV Assay
Identify the presence and activity of a high-risk HPV infection
in their lives, relatively few will go on to develop cancer. 1 Thus, an optimal screening strategy should identify cervical cancer precursors likely to progress to invasive cancers, while avoiding detection and unnecessary treatment of transient HPV infection and its associated noncancerous lesions.2 With the extension of recommended intervals between cervical cancer screenings, it has become all the more important to accurately identify at-risk patients.
A Targeted Approach 3-7
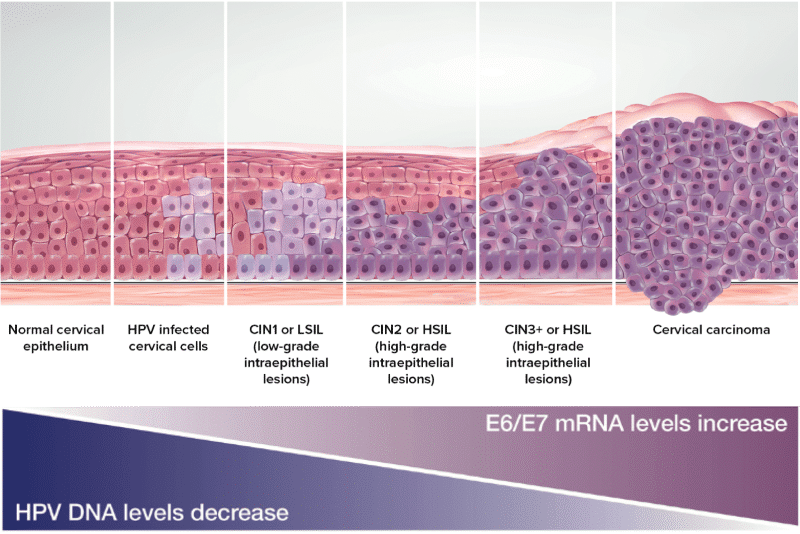
Cervical Cancer Progression Model
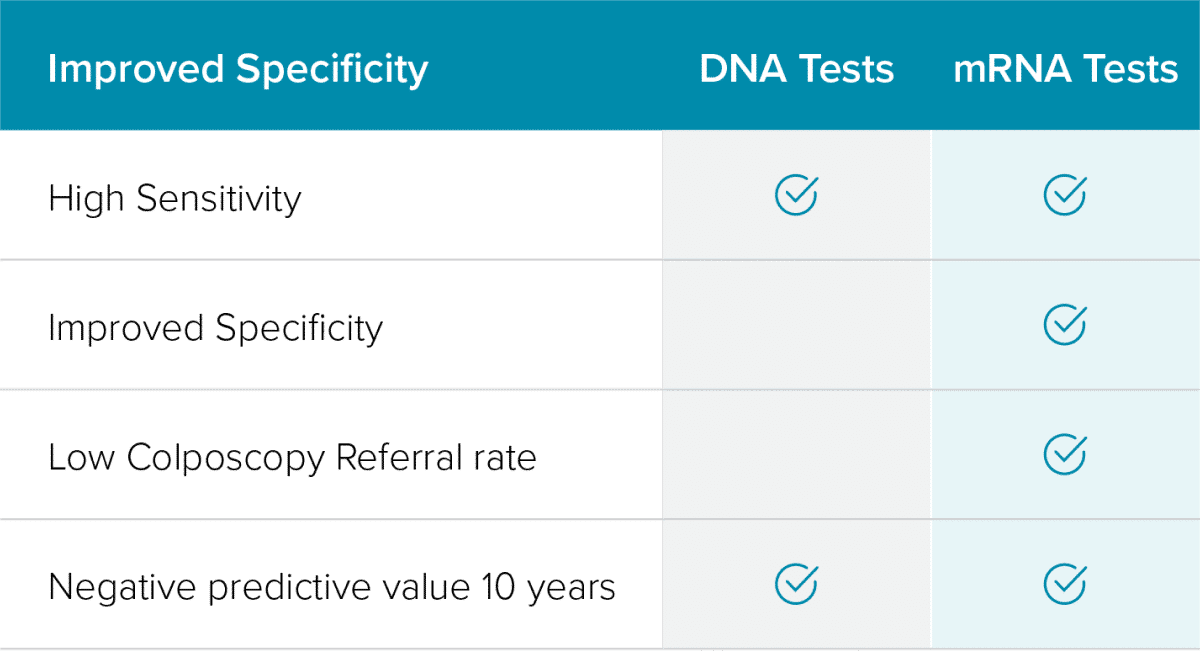
Maximizing the Benefits and Minimizing the Harms 2,3,8-19
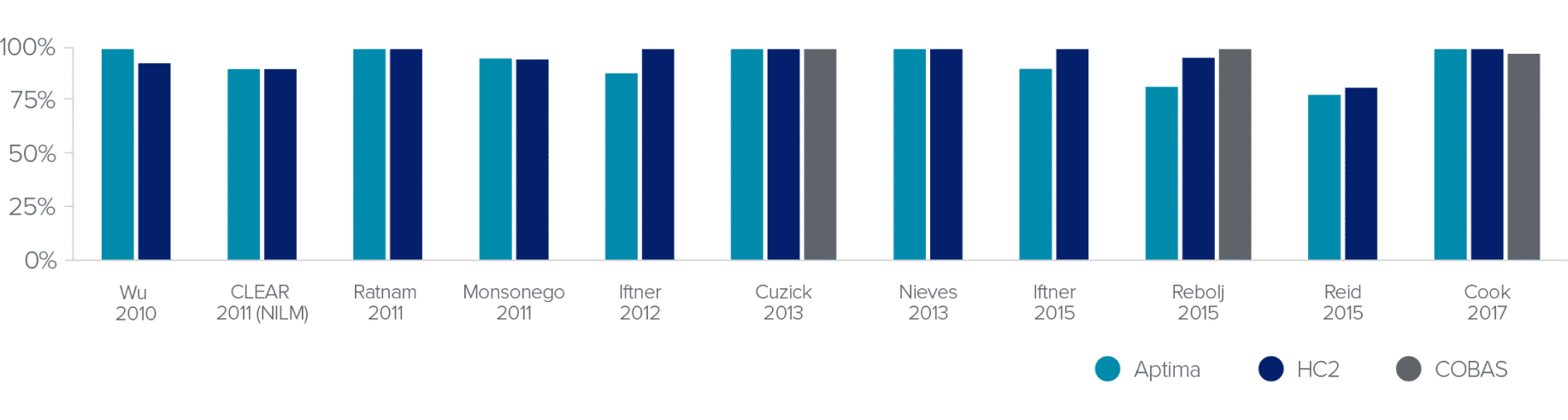
HPV Test Clinical Sensitivity for ≥CIN3
The Aptima® HPV assay provides the same excellent sensitivity you’ve come to expect from DNA-based tests.
Screening Population
HPV Test Clinical Sensitivity for ≥CIN2
mRNA-based tests show equivalent sensitivity to DNA-based tests with superior specificity.
Screening Population
- Minimize difficult patient conversations
- Reduce the potential for overtreatment
- Minimize the unnecessary cost to the patient
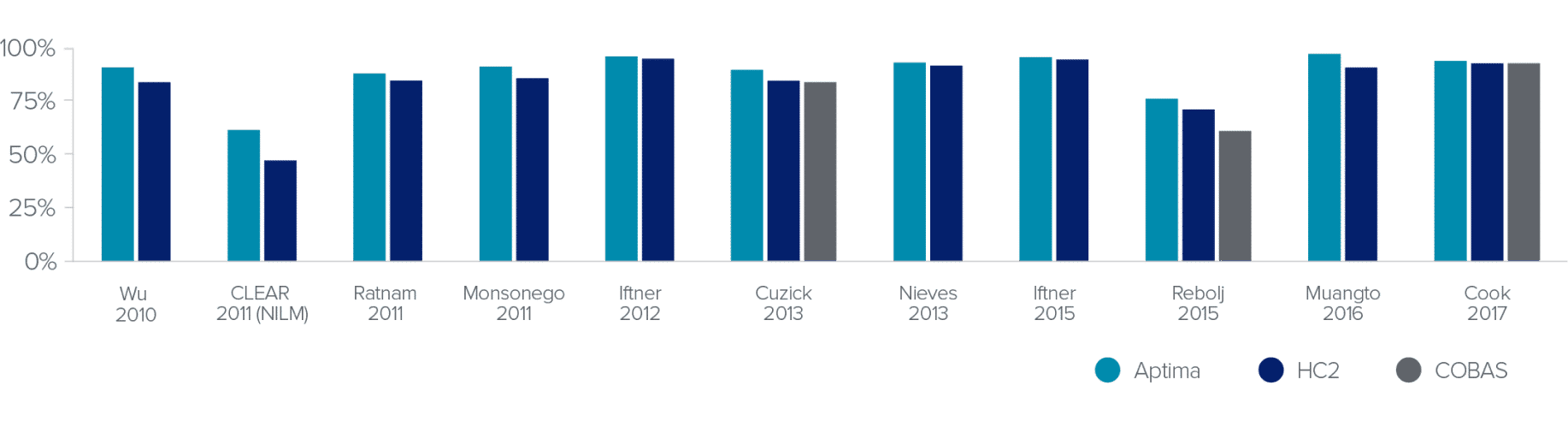
HPV Viral mRNA 20
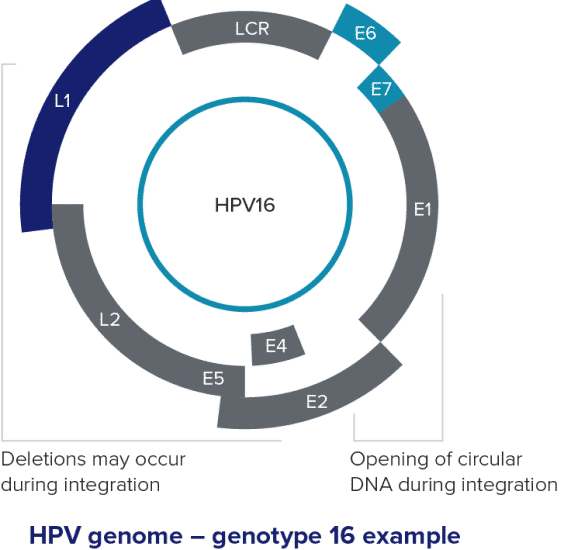
- Tests that target only the L1 gene are detecting an area that is not needed for disease progression and that can be deleted during integration.
- As HPV DNA integrates into human DNA the L1 region can be deleted.
- HPV assays that only target the L1 region are at risk for false negative results.

Years of Long-Term Results16,17, 21-23

Reid - 3 Years
“After 3-years of follow-up, women negative by either HPV test had a very low risk for CIN2+ (<0.3%)…”
Cook- 4 Years
“There was no significant difference in CIN2+ detection for AHPV vs. HC2 at baseline or at 48 months.”
Forslund - 7 Years
“The observed performance of the HPV-mRNA assay suggests that the evaluated assay is non-inferior to HPV-DNA testing and can be used in cervical screening programs that target women above 30 years of age for 5-7 yearly screening.”
Strang - 10 Years
“Our study found that, among this population, a negative baseline HPV test by any one of the three assays used in the HPV FOCAL Trial (HC2, CG, or AHPV), resulted in statistically similar CIN2+ and CIN3+ detection over ten years follow-up.”